Table of Contents
- What is External Secrets Operator?
- What Problem does it solve?
- How to setup External Secrets Operator in GKE
- Author Work Story
What is External Secrets Operator?
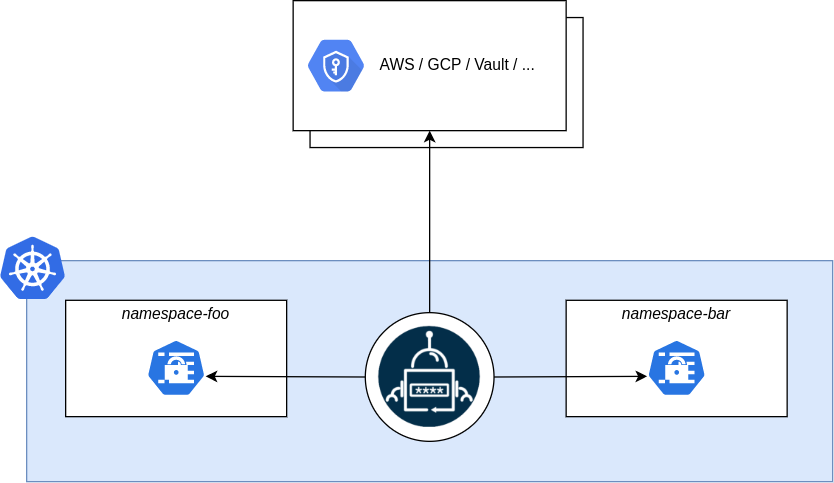
External Secrets Operator is a Kubernetes operator that integrates external secret management systems like AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault, Google Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, IBM Cloud Secrets Manager, CyberArk Conjur, Pulumi ESC and many more. The operator reads information from external APIs and automatically injects the values into a Kubernetes Secret.
You can read more about it here https://external-secrets.io/v0.16.1
What Problem does it solve?
It solves the problem of consistency of your secrets across different environments.
Take for example you have a database password that you store in AWS/GCP secrets manager. You also have that same database password stored as k8s secrets in 5 different namespaces as well. If you update the password you’d have to update it in 6 different places. It would be a pain to have to update everywhere. That’s where the External Secrets Operator makes life so easy.
With External Secrets Operator you’ll make the source of truth be secrets manager. You’ll define a manifest that has a reference to the secret manager secret and the k8s secret will be created with that secret. Please see the example below.
apiVersion: external-secrets.io/v1alpha1
kind: ExternalSecret
metadata:
name: "hello-world"
spec:
# This has permission to query Secrets Manager
secretStoreRef:
name: secret-store-name
kind: SecretStore # or ClusterSecretStore
# RefreshInterval is the amount of time before the values reading again from the SecretStore provider
# Valid time units are "ns", "us" (or "µs"), "ms", "s", "m", "h" (from time.ParseDuration)
# May be set to zero to fetch and create it once
refreshInterval: "1h"
# the target describes the secret that shall be created
# there can only be one target per ExternalSecret
target:
# The secret name of the resource
# Defaults to .metadata.name of the ExternalSecret
# It is immutable
name: my-secret # It'll appear as secret name when you run `kubectl get secrets`
# Data defines the connection between the Kubernetes Secret keys and the Provider data
data:
- secretKey: secret-key-to-be-managed # Name of the secret
remoteRef:
key: provider-key # name of the Secrets manager secret name
version: provider-key-version # The version of the Secrets manager secret
How to setup External Secrets Operator in GKE
Lets create a script called run-setup.sh
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud projects list --filter="$(gcloud config get-value project)" --format="value(PROJECT_ID)")
PROJECT_NUMBER=$(gcloud projects list --filter="$(gcloud config get-value project)" --format="value(PROJECT_NUMBER)")
NAMESPACE=external-secrets
KSA_NAME=external-secrets # This will be created by
CLUSTER_STORE_MANIFEST=cluster-store.yaml
EXTERNAL_SECRET_MANIFEST=external-secret.yaml
GCP_SECRET_NAME=my-secret
K8S_SECRET_NAME=my-k8s-secret-yay
# Installing the helm chart for external secrets. You don't need to be an expert in helm chart
# but I heavily suggest you learn the basics of it.
# Check out Ahmed Elfakharany course on it on udemy
# https://www.udemy.com/share/105eEs3@HJ8aCtyHLG8Xg2rrdoCuepCPztyv_F_KAyXhJXzsKwD-zRl_ojP7th1zyt-_m9co/
helm repo add external-secrets https://charts.external-secrets.io
helm install external-secrets \
external-secrets/external-secrets \
-n $NAMESPACE \
--create-namespace \
--set installCRDs=true
# Workload Federation. Role is applied directly to KSA
# See https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/how-to/workload-identity#configure-authz-principals
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding projects/$PROJECT_ID \
--role=roles/secretmanager.secretAccessor \
--member=principal://iam.googleapis.com/projects/$PROJECT_NUMBER/locations/global/workloadIdentityPools/$PROJECT_ID.svc.id.goog/subject/ns/$NAMESPACE/sa/$KSA_NAME \
--condition=None
echo -n "my super secret data" | gcloud secrets create $GCP_SECRET_NAME --data-file=-
# ClusterSecretStore represents a secure external location for storing secrets. In actuality it'll make a api call to the Secrets manager to get the secret value
cat > $CLUSTER_STORE_MANIFEST << EOL
---
apiVersion: external-secrets.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterSecretStore
metadata:
name: gcp-store
spec:
provider:
gcpsm:
projectID: $PROJECT_ID
EOL
cat > $EXTERNAL_SECRET_MANIFEST << EOL
---
apiVersion: external-secrets.io/v1beta1
kind: ExternalSecret
metadata:
name: my-external-secret
spec:
refreshInterval: 1h # rate SecretManager pulls the secrets manager
secretStoreRef:
kind: ClusterSecretStore
name: gcp-store # name of the ClusterSecretStore (or kind specified)
target:
name: $K8S_SECRET_NAME # name of the k8s Secret to be created
creationPolicy: Owner
data:
- secretKey: SECRET_KEY
remoteRef:
version: "1" # Version of the secret. If not specified it'll use the latest
key: $GCP_SECRET_NAME # name of the GCP Secrets Manager name
EOL
# We are going to make the cluster store
kubectl apply -f $CLUSTER_STORE_MANIFEST
# We are going to create the external-secret
kubectl apply -f $EXTERNAL_SECRET_MANIFEST
If everything went to plan then a Kubernetes Secret called my-k8s-secret-yay with a data field called SECRET_KEY should have been created.
$ kubectl get secrets/my-k8s-secret-yay -o json | jq -r .data.SECRET_KEY | base64 -d && echo ""
my super secret data
Author Work Story
I’m using helm charts and argo-cd to manage my k8s clusters. I needed a way to have some consistency between secrets that were in secret manager and the k8s secrets. I started off using helm secrets. It solved the problem of consistency between my k8s secrets and GCP secret manager secrets. However the cracks began to show after I started using argo-cd to control the Continuous Delivery of my apps. It became quickly apparent supporting helm secrets wasn’t going to work out as seen in the documentation to integrate helm secrets with argo-cd. Yikes!
Being able to store the references to GCP secret manager secrets in git without risk of exposing the sensitive information was a Godsend. Give external secrets operator a try and star/contribute to the project if you can.
Cheers!